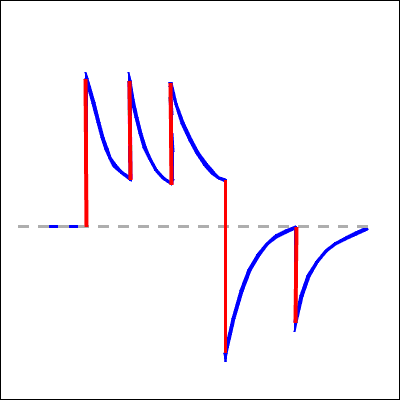
Nystagmus

So the patient generates a second saccade, and third etc., which also drift back.
If the patient looks to the left the same thing happens.
This rhythmic eye movement is called nystagmus.
Nystagmus consists of a quick phase (saccades) and a slow phase (in this case a drift back to center)
This particular form of nystagmus is called gaze paretic nystagmus because the patient cannot hold an eccentric gaze. It is characterized by:
- the drift is exponential
- the drift direction is different depending on where the patient looks.